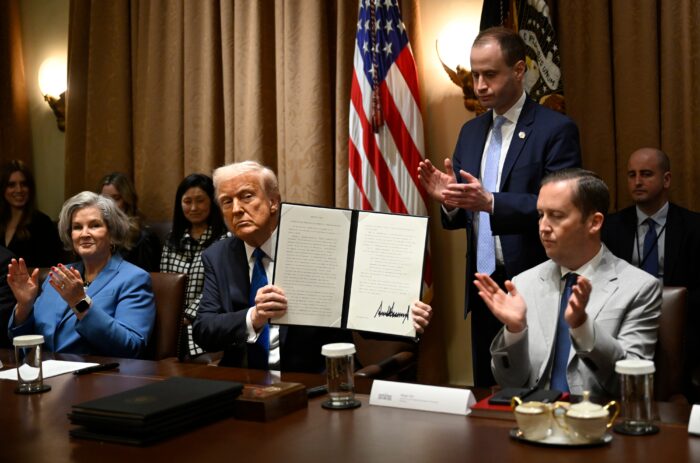
President Donald Trump, flanked by Merck CEO Kenneth Frazier, left, and Celgene CEO Robert Hugin speaks during a meeting with pharmaceutical company CEOs.
redo Jump to...
print Print...
Trump told them the government was paying “astronomical” prices for medicines in its [medicare and medicaid] health programs for older, disabled and poor people and said he would soon appoint a new U.S. Food and Drug Administration leader.
“We’re going to streamline the FDA,” President Trump said in a statement, referring to the regulatory agency responsible for vetting that new drugs are safe and effective.
…Attending the meeting were top executives [from pharmaceutical companies] Merck, Johnson & Johnson, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Amgen and Switzerland’s Novartis, as well as the head of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) lobbying group.
According to a transcript of the televised portion of the meeting, Amgen Chief Executive Officer Robert Bradway promised to add 1,600 U.S. jobs at his California-based biotechnology company this year.
Amgen clarified in an email that it currently employs around 20,000 people worldwide, including 12,000 in the United States, and said the 1,600 includes new staff as well as hires to address attrition.
Celgene, Lilly, Merck and Amgen said by email after the meeting that they were encouraged by Trump’s focus on innovation, tax reform and the need for a more value-driven health care system.
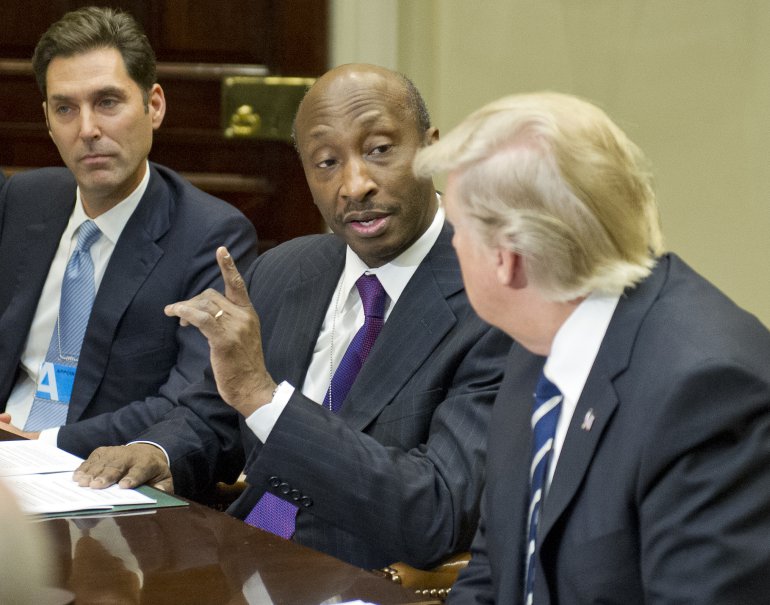

Kenneth C. Frazier, Chairman and CEO of Merck & Co makes remarks to President Trump during a meeting in the Roosevelt Room of the White House on January 31, 2017.
Lilly said discussion topics also included stronger trade agreements and removing “outdated regulations that drive up costs and slow innovation.”
PhRMA echoed those points in its own post-meeting statement, adding that the policies, if enacted, would result in up to 350,000 new jobs over the next 10 years.
“Tax, deregulation – those are things that could really help us expand operations,” Lilly CEO Dave Ricks said.
Officials at Novartis and J&J did not immediately respond to requests for additional comment. …
“We have to get prices down for a lot of reasons. We have no choice, for Medicare and Medicaid,” President Trump said, citing the nation’s government insurance programs for the elderly, the poor and the disabled.
President Trump also said currency devaluation by other countries had increased drugmakers’ outsourcing their production, and he called on the companies to make more of their products in the United States.
Foreign countries must pay a fair share for drug development costs, he added. “We’re going to end global freeloading.”
The United States typically pays more for drugs than any other developed nation….
High drug prices have become a national issue during the past two years as healthcare costs have risen. Mr. Trump spooked pharmaceutical and biotech investors by saying on Jan. 11, before his inauguration, that drug companies were “getting away with murder” on what they charged the government for medicine and that he would do something about it. …
[“The U.S. drug companies have produced extraordinary results for our country, but the pricing has been astronomical for our country,” the president said after meeting with drug industry executives on Tuesday at the White House.The U.S. needs to “do better” for Americans, Mr. Trump added, promising to boost industry competition to bring down prices. ]
(Additional reporting by Eric Beech, Ben Hirschler, John Miller, Chuck Mikolajczak, Rodrigo Campos, Susan Heavey and Caroline Humer; Editing by Lisa Von Ahn and Cynthia Osterman)
Reprinted here for educational purposes only. May not be reproduced on other websites without permission from Thomson Reuters. Visit the website at Reuters.com.
Questions
1. The first paragraph of a news article should answer the questions who, what, where and when. List the who, what, where and when of this news item. (NOTE: The remainder of a news article provides details on the why and/or how.)
2. What did President Trump tell the heads of the companies he would do to help them?
3. a) What is the role of the FDA?
b) What did the president say about the FDA?
4. a) How many people does Amgen employ in the U.S.?
b) How many jobs did the CEO promise to add this year?
5. a) What did Eli Lilly CEO Dave Ricks say would help his company expand operations?
b) What negative effect does outdated regulation have on the industry (or any industry)?
c) Define deregulation.
6. What overall reaction did the executives have to the meeting with President Trump?
7. a) What do you think of President Trump’s meeting with the pharmaceutical company CEOs? (will he get drug prices lowered?) Please explain your answer.
b) What do you think of President Trump’s vow to reduce federal government regulations as a way to help businesses – including the action he took this week to reduce regulations for small businesses? Please explain your answer.
Background
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA or USFDA) is an agency of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, one of the U.S. federal executive departments.
- The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the regulation and supervision of food safety, tobacco products, dietary supplements, prescription and over-the-counter pharmaceutical drugs (medications), vaccines, biopharmaceuticals, blood transfusions, medical devices, electromagnetic radiation emitting devices (ERED), animal foods & feed, veterinary products, and cosmetics.
- The FDA also enforces other laws, notably Section 361 of the Public Health Service Act and associated regulations, many of which are not directly related to food or drugs. These include sanitation requirements on interstate travel and control of disease on products ranging from certain household pets [etc.].
- The FDA is led by the Commissioner of Food and Drugs, appointed by the President with the advice and consent of the Senate. The Commissioner reports to the Secretary of Health and Human Services. The current Commissioner is Dr. Robert Califf. He was confirmed as Commissioner in February (2016).
- The FDA has its headquarters in Maryland, and also has 223 field offices and 13 laboratories located throughout the 50 states, the United States Virgin Islands, and Puerto Rico. In 2008, the FDA started opening offices in foreign countries, including China, India, Costa Rica, Chile, Belgium, and the United Kingdom.
- The FDA’s federal budget request for fiscal year (FY) 2012 totaled $4.36 billion, while the proposed 2014 budget was $4.7 billion.
- About $2 billion of this budget is generated by user fees. Pharmaceutical firms pay the majority of these fees, which are used to expedite drug reviews.
- Most federal laws concerning the FDA are part of the Food, Drug and Cosmetic Act, (first passed in 1938 and extensively amended since)
- Since the Family Smoking Prevention and Tobacco Control Act became law in 2009, the FDA also has had the authority to regulate tobacco products. (from wikipedia)
Daily “Answers” emails are provided for Daily News Articles, Tuesday’s World Events and Friday’s News Quiz.