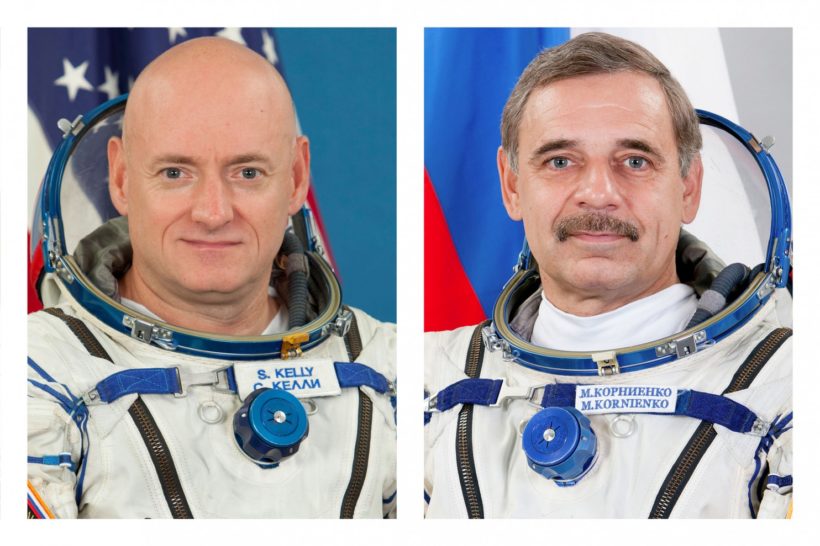
American astronaut Scott Kelly (left) and Russian cosmonaut Mikhail Kornienko.
redo Jump to...
print Print...
(by Dmitry Lovetsky and Jim Heintz, Associated Press) BAIKONUR, Kazakhstan — Two Russians and an American [traveled] to the International Space Station on Saturday, beginning what is to be a year away from Earth for two of them.
Mikhail Kornienko and Scott Kelly are to spend 342 days aboard the orbiting laboratory, about twice as long as a standard mission on the station. Russia’s Gennady Padalka is beginning a six-month stay.
The three astronauts entered the station about eight hours after launching from Russia’s manned space facility in Kazakhstan. They were embraced by American Terry Virts and Russia’s Anton Shkaplerov who along with Italian Samantha Cristoforetti have been aboard since late November.
The trip is NASA’s first attempt at a one-year spaceflight; four Russians have spent a year or more in space, all on the Soviet-built Mir space station.
The stay is aimed at measuring the effects of a prolonged period of weightlessness on the human body, a step toward possible missions to Mars or beyond.
Kelly’s identical twin Mark, a retired astronaut, agreed to take part in many of the same medical experiments as his orbiting sibling to help scientists see how a body in space compares with its genetic double on Earth. They are 51.
Kelly and Kornienko, 54, will remain on board until next March. During that time, they will undergo extensive medical experiments, and prepare the station for the anticipated 2017 arrival of new U.S. commercial crew capsules. That means a series of spacewalks for Kelly, which will be his first.
The two men also will oversee the comings and goings of numerous cargo ships, as well as other Russian-launched space crews and an expected September visit from singer Sarah Brightman on a “space tourist” trip.
Doctors are eager to learn what happens to Kelly and Kornienko once they surpass the usual six-month stay for space station residents.
Bones and muscles weaken in weightlessness, as does the immune system. Body fluids also shift into the head when gravity is absent, putting pressure on the brain and the eyes, impairing vision for some astronauts in space.
The yearlong stint will allow doctors to assess whether such conditions are aggravated by a long spell in space or whether they reach a point of stasis or even taper off.
As space officials look to longer missions, the International Space Station’s future appears ensured until at least 2024.
Last year, as tensions between Russia and the United States grew amid the dispute over Russia’s role in Ukraine, Deputy Prime Minister Dmitry Rogozin had said Moscow aimed to exit the project in 2020.
But Russian space agency director Igor Komarov told a post-launch news conference in Baikonur that his agency and NASA have agreed to continue using the station until 2024.
In addition, “Roscosmos and NASA will work on a program for a future orbiting station. We will think about discuss joint projects,” he said. Just last month, Roscosmos said it foresaw creating a Russian station for use after 2024.
NASA has never flown anyone longer than seven consecutive months. The Russians hold the world record of 14 months in space, set by Valery Polyakov aboard the former Mir space station in 1994-95. Several other Russians spent between eight and 12 months at Mir. All but one of those long-timers are still alive.
A year in space will carry not only physical challenges, but emotional ones as well.
A day before the launch, Kornienko said he would long for the sights of nature. Even on his mission in 2010, which was half as long, he said he had asked to be sent a calendar with photos of rivers and woods.
Kelly said he thought one of the biggest challenges would be to pace himself mentally so he could remain energetic during the year aboard the laboratory. …
First published March 28, 2015. Reprinted here for educational purposes only. May not be reproduced on other websites without permission from the Associated Press.
Questions
1. a) What is significant about astronaut Scott Kelly’s trip to the ISS?
b) Why does this trip not hold the same significance for Russian cosmonaut Mikhail Kornienko?
2. a) What is the purpose of the two astronaut’s mission?
b) What do doctors want to determine from the yearlong mission?
c) What effects does the absence of gravity have on a body?
3. How will astronaut Scott Kelly’s twin brother help doctors with the experiments?
4. What will the astronauts do during their yearlong stay?
5. How would you view a yearlong stay on the ISS? Explain your answer.
Background
The International Space Station:
- The International Space Station (ISS) is a space station, or a habitable artificial satellite, in low Earth orbit. Its first component was launched in 1998. Now the largest artificial body in orbit, it can often be seen with the naked eye from Earth.
- The ISS program is a joint project among five participating space agencies: NASA, Roscosmos (Russia), JAXA (Japan), ESA (Europe), and CSA (Canada).
- The ownership and use of the space station is established by intergovernmental treaties and agreements.
- The station is divided into two sections, the Russian Orbital Segment (ROS) and the United States Orbital Segment (USOS), which is shared by many nations. As of January 2014, the American portion of ISS was funded until 2024.
- ISS is the ninth space station to be inhabited by crews, following the Soviet and later Russian Salyut, Almaz, and Mir stations as well as Skylab from the US. The ISS has been continuously occupied for 14 years and 148 days since the arrival of Expedition 1 on 2 November 2000. This is the longest continuous human presence in space, having surpassed the previous record of 9 years and 357 days held by Mir.
- After the US Space Shuttle program ended in 2011, Soyuz rockets became the only provider of transport for astronauts at the International Space Station, and Dragon became the only provider of bulk cargo-return-to-Earth services (downmass capability of Soyuz capsules is very limited).
- The ISS serves as a microgravity and space environment research laboratory in which crew members conduct experiments in biology, human biology, physics, astronomy, meteorology and other fields. The station is suited for the testing of spacecraft systems and equipment required for missions to the Moon and Mars. (from wikipedia)
Resources
For information and video on the ISS from NASA’s website, go to nasa.gov/mission_pages/station/main/index.html.
For NASA’s interactive reference guide to the space station, go to nasa.gov/externalflash/ISSRG/index.html.
For Space Station International Agreements, go to Europe’s: esa.int/Our_Activities/Human_Spaceflight/International_Space_Station/International_Space_Station_legal_framework
Watch an AP report:
Daily “Answers” emails are provided for Daily News Articles, Tuesday’s World Events and Friday’s News Quiz.