ACLU: Amazon shouldn’t sell face-recognition tech to police
Daily News Article — Posted on May 23, 2018
(by Gene Johnson, Associated Press at ABC News) – The American Civil Liberties Union and other privacy activists are asking Amazon to stop marketing a powerful facial recognition tool to police, saying law enforcement agencies could use the technology to “easily build a system to automate the identification and tracking of anyone.”
The tool, called Rekognition, is already being used by at least one agency — the Washington County Sheriff’s Office in Oregon — to check photographs of unidentified suspects against a database of mug shots from the county jail, which is a common use of such technology around the country.
But privacy advocates have been concerned about expanding the use of facial recognition to body cameras worn by officers or safety and traffic cameras that monitor public areas, allowing police to identify and track people in real time.
The tech giant’s entry into the market could vastly accelerate such developments, the privacy advocates fear. [Their concern is that it would have] potentially dire consequences for minorities who they say are already arrested at disproportionate rates, immigrants who may be in the country illegally or political protesters.
“People should be free to walk down the street without being watched by the government,” the groups wrote in a letter to Amazon on Tuesday. “Facial recognition in American communities threatens this freedom.”
Amazon released Rekognition in late 2016, and the sheriff’s office in Washington County, west of Portland, became one of its first law enforcement agency customers. A year later, deputies were using it about 20 times per day — for example, to identify burglary suspects in store surveillance footage. Last month, [several months after acquiring Rekognition] the agency adopted policies governing its use, noting that officers in the field can use real-time face recognition to identify suspects who are unwilling or unable to provide their own ID, or if someone’s life is in danger.
“We are not mass-collecting. We are not putting a camera out on a street corner,” said Deputy Jeff Talbot, a spokesman for the sheriff’s office. “We want our local community to be aware of what we’re doing, how we’re using it to solve crimes — what it is and, just as importantly, what it is not.”
It cost the sheriff’s office just $400 to load 305,000 booking photos into the system and $6 per month in fees to continue the service, according to an email obtained by the ACLU under a public records request.
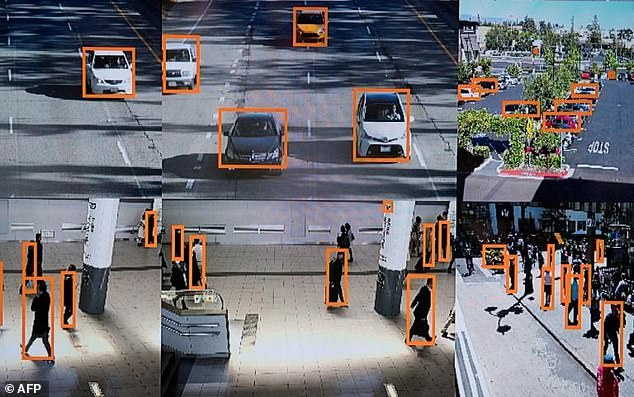
Facial recognition is used by many technology companies, but activists say Amazon’s system could lead to dangerous surveillance powers for law enforcement.
Amazon Web Services did not answer emailed questions about how many law enforcement agencies are using Rekognition, but in a written statement the company said it requires all of its customers to comply with the law and to be responsible in the use of its products.
The statement said some agencies have used the program to find abducted people, and amusement parks have used it to find lost children. British broadcaster Sky News used Rekognition to help viewers identify celebrities at the royal wedding of Prince Harry and Meghan Markle last weekend.
Last year, the Orlando, Florida, Police Department announced it would begin a pilot program relying on Amazon’s technology to “use existing City resources to provide real-time detection and notification of persons-of-interest, further increasing public safety.”
Orlando has a network of public safety cameras, and in a presentation posted to YouTube this month , Ranju Das, who leads Amazon Rekognition, said Amazon would receive feeds from the cameras, search them against photos of people being sought by law enforcement and notify police of any hits.
“It’s about recognizing people, it’s about tracking people, and then it’s about doing this in real time, so that the law enforcement officers … can be then alerted in real time to events that are happening,” he said.
The Orlando Police Department declined to make anyone available for an interview about the program, but said in an email to The Associated Press that the department “is not using the technology in an investigative capacity or in any public spaces at this time.”
“The purpose of a pilot program such as this, is to address any concerns that arise as the new technology is tested,” the statement said. “Any use of the system will be in accordance with current and applicable law. We are always looking for new solutions to further our ability to keep the residents and visitors of Orlando safe.”
The letter to Amazon followed public records requests from ACLU chapters in California, Oregon and Florida. More than two dozen organizations signed it, including the Electronic Frontier Foundation and Human Rights Watch.
Clare Garvie, an associate at the Center on Privacy and Technology at Georgetown University Law Center, said part of the problem with real-time face recognition is its potential impact on free-speech rights.
While police might be able to videotape public demonstrations, face recognition is not merely an extension of photography but a biometric measurement — more akin to police walking through a demonstration and demanding identification from everyone there.
Amazon’s technology isn’t that different from what face recognition companies are already selling to law enforcement agencies. But its vast reach and its interest in recruiting more police departments to take part raise concerns, she said.
“This raises very real questions about the ability to remain anonymous in public spaces,” Garvie said.
From a report by Associated Press published at ABC News. Reprinted here for educational purposes only. May not be reproduced on other websites without permission from ABC News.
Questions
1. The first paragraph of a news article should answer the questions who, what, where and when. List the who, what, where and when of this news item. (NOTE: The remainder of a news article provides details on the why and/or how.)
2. a) For what reason are the privacy groups asking Amazon to stop marketing the technology to police? Be specific.
b) Why are they concerned about Amazon’s entry into the facial recognition tech market?
3. How does the Washington County Sheriff’s Office in Oregon use Rekognition? Be specific.
4. a) How did Deputy Jeff Talbot try to reassure residents about the department’s use of the Amazon technology?
b) Deputy Talbot and the sheriff’s department appear to have good intentions. Why might his assurances not dispel residents’ concerns?
5. a) How did Amazon respond to questions and concerns?
b) For what purposes did Amazon say law enforcement agencies use Rekognition?
c) What is your reaction to Amazon’s response and explanation?
6. Re-read para. 11-15 regarding the Orlando Police Department’s program using Amazon’s facial recognition technology. Do you think “improving public safety” is worth giving up all right to privacy / anonymity? Explain your answer.
7. The ACLU is opposed to Amazon selling their facial recognition to police departments because “it would have potentially dire consequences for minorities who they say are already arrested at disproportionate rates, immigrants who may be in the country illegally or political protesters.”
Other privacy advocates are also concerned for average citizens who are just going about their daily lives. Some are also concerned that Amazon is gaining more and more information about all of us. Amazon already knows all of your likes/dislikes (browsing/purchasing).
a) If Amazon controls the software for police departments across the country, would that concern you? Why or why not?
b) The ACLU is asking Amazon not to sell to police departments. Do you think they should also ask Amazon not to sell to news organizations, music or sporting venues or other non-law enforcement companies? Explain your answer.
8. Why do you think the ACLU is only asking Amazon to not sell Rekognition to the police? Why aren’t they asking Amazon not to sell it to corporations?
9. Possibly more troubling than police, who have legal restrictions in using this technology, is the fact that individuals and corporations are using it. (Entities that have less regulation and oversight than the police.) What is your thought on the use of this technology by those other than the police?
Background
New technologies are radically advancing our freedoms, but they are also enabling unparalleled invasions of privacy. National and international laws have yet to catch up with the evolving need for privacy that comes with new digital technologies. Respect for individuals' autonomy, anonymous speech, and the right to free association must be balanced against legitimate concerns like law enforcement. EFF fights in the courts and Congress to extend your privacy rights into the digital world, and works with partners around the globe to support the development of privacy-protecting technologies.
Your cell phone helps you keep in touch with friends and family, but it also makes it easier for security agencies to track your location.
Your Web searches about sensitive medical information might seem a secret between you and your search engine, but companies like Google are creating a treasure trove of personal information by logging your online activities, and making it potentially available to any party wielding enough cash or a subpoena... (from Electronic Frontier Foundation)
