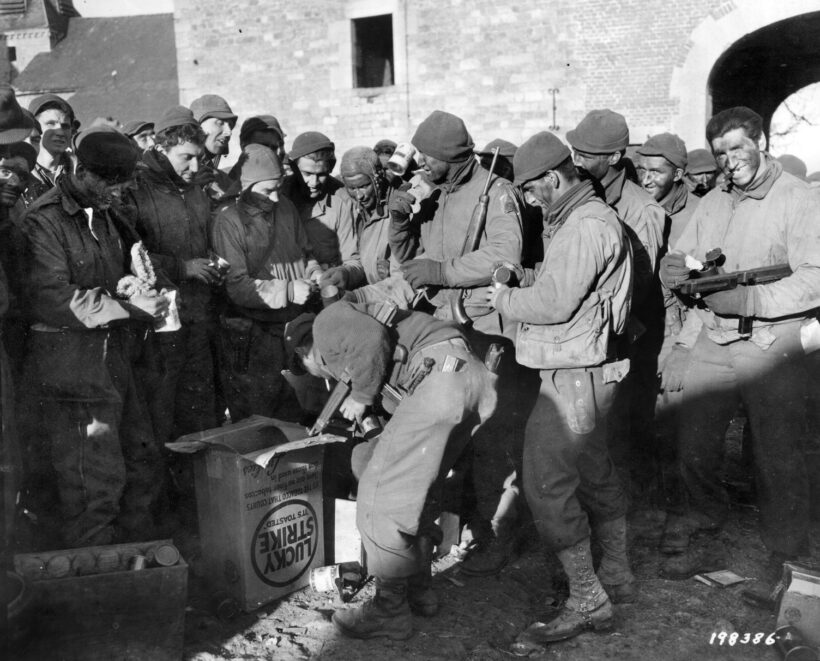
Their faces blackened as camouflage during their night march through German lines, men of ‘Hogan’s 400’ pass out Lucky Strike cigarettes to one another and celebrate their survival from the desperate combat that characterized the Battle of the Bulge. (Warfare History Network)
redo Jump to...
print Print...
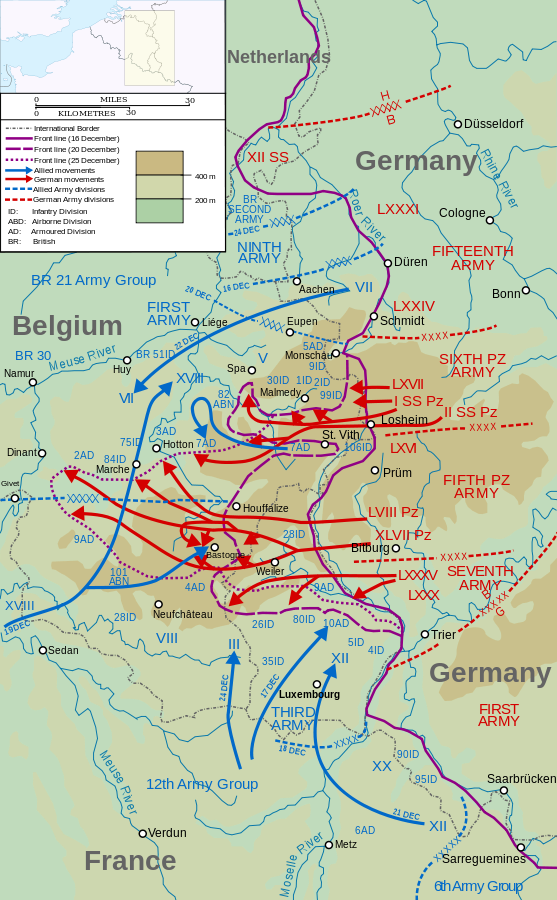
(from U.S. Army Center of Military History) — In late 1944, during the wake of the Allied forces’ successful D-Day invasion of Normandy, France, it seemed as if the Second World War was all but over. On Dec. 16, with the onset of winter, the German army launched a counteroffensive that was intended to cut through the Allied forces in a manner that would turn the tide of the war in Hitler’s favor. The battle that ensued is known historically as the Battle of the Bulge. The courage and fortitude of the American Soldier was tested against great adversity. Nevertheless, the quality of his response ultimately meant the victory of freedom over tyranny.
Early on the misty winter morning of Dec. 16, 1944, more than 200,000 German troops and nearly 1,000 tanks launched Adolf Hitler’s last bid to reverse the ebb in his fortunes that had begun when Allied troops landed in France on D-Day. Seeking to drive to the coast of the English Channel and split the Allied armies as they had done in May 1940, the Germans struck in the Ardennes Forest, a 75-mile stretch of the front characterized by dense woods and few roads, held by four inexperienced and battle-worn American divisions stationed there for rest and seasoning.
After a day of hard fighting, the Germans broke through the American front, surrounding most of an infantry division, seizing key crossroads, and advancing their spearheads toward the Meuse River, creating the projection that gave the battle its name.
Stories spread of the massacre of Soldiers and civilians at Malmedy and Stavelot, of paratroopers dropping behind the lines, and of English-speaking German soldiers, disguised as Americans, capturing critical bridges, cutting communications lines, and spreading rumors. For those who had lived through 1940, the picture was all too familiar. Belgian townspeople put away their Allied flags and brought out their swastikas. Police in Paris enforced an all-night curfew. British veterans waited nervously to see how the Americans would react to a full-scale German offensive, and British generals quietly acted to safeguard the Meuse River’s crossings. Even American civilians, who had thought final victory was near were sobered by the Nazi onslaught.
But this was not 1940. The supreme Allied commander, Gen. Dwight D. Eisenhower rushed reinforcements to hold the shoulders of the German penetration. Within days, Lt. Gen. George S. Patton Jr. had turned his Third U.S. Army to the north and was counterattacking against the German flank.
But the story of the Battle of the Bulge is above all the story of American Soldiers. Often isolated and unaware of the overall picture, they did their part to slow the Nazi advance, whether by delaying armored spearheads with obstinate defenses of vital crossroads, moving or burning critical gasoline stocks to keep them from the fuel-hungry German tanks, or coming up with questions on arcane Americana to stump possible Nazi infiltrators.
At the critical road junctions of St. Vith and Bastogne, American tankers and paratroopers fought off repeated attacks, and when the acting commander of the 101st Airborne Division in Bastogne (Brigadier General Anthony McAuliffe) was summoned by his German adversary to surrender, he simply responded, “Nuts!” (Read about it here.)
Within days, Patton’s Third Army had relieved Bastogne, and to the north, the 2nd U.S. Armored Division stopped enemy tanks short of the Meuse River on Christmas. Through January, American troops, often wading through deep snow drifts, attacked the sides of the shrinking bulge until they had restored the front and set the stage for the final drive to victory (on Jan. 25, 1945).
Never again would Hitler be able to launch an offensive in the west on such a scale. An admiring British Prime Minister Sir Winston Churchill stated,
“This is undoubtedly the greatest American battle of the war and will, I believe, be regarded as an ever-famous American victory.”
Indeed, in terms of participation and losses, the Battle of the Bulge is arguably the greatest battle in American military history.
Courtesy of the U.S. Army Battle of the Bulge page.
Questions
NOTE: Before answering the following questions, read the “Background” and watch the videos under “Resources” below.
1. How long did the Battle of the Bulge last?
2. What was Hitler’s aim for what became known as the Battle of the Bulge?
3. How did the Germans use their English-speaking soldiers?
4. a) Who was the supreme Allied commander in Europe?
b) Who led the Third U.S. Army?
5. What did American soldiers do to slow the Nazi advance?
6. a) Define gallant and valor as words that were used to describe the American soldiers who fought in the Battle of the Bulge.
b) Why would you use these two words specifically to describe the American soldiers who fought in the Battle of the Bulge?
7. Consider the information found in the links, as well as the videos. What impresses/inspires you most about U.S. (and Allied) troops beating the Nazis in this campaign?
Background
The Battle of the Bulge:
One of the most gallant combat actions in the Battle of the Bulge was that of an intelligence and reconnaissance (I&R) platoon’s defense near Lanzerath, Belgium, on the first day of the battle. For their exploits, the I&R Platoon, 394th Infantry Regiment, 99th Infantry Division, would later become “the most heavily decorated platoon for a single (enemy engagement) in World War II.” The 18 men of the I&R platoon had inflicted between 400 and 500 casualties, decimating an entire battalion of the German 3d Parachute Division.
Platoon leader Lyle Bouck later said “I felt like what I did was a failure.” because he and his men were ultimately captured – despite the fact that they had prevented a force of over 5,000 Germans from advancing for eight crucial hours. Read an overview at: nationalww2museum.org and more details at fas.org.
- The Germans called it the “Operation Watch on the Rhine.” the French named it the “Battle of the Ardennes.” And the Western Allies termed it the “Ardennes Countero ensive.”
- But because of the way the map of Western Europe looked at the height of the battle, it became known to history as the “Battle of the Bulge.”
- It was the winter of 1944–1945, months before the war in Europe would end (on May 8, 1945).
- Despite the protestations of his generals, Adolf Hitler decided on one final attempt to turn World War II in favor of his German Third Reich. For this, he ordered resources diverted from other battle fronts — including his losing campaign against the Russians in the east.
- The Allies were caught off guard, as Hitler had hoped. Thousands of U.S. troops were surrounded at one point. In the end, the Allies committed enough troops that the tired, ill- equipped German army was overwhelmed.
- Indeed, the Battle of the Bulge was an important turning point in the war in the Allies’ favor, but it was not without its cost. The Battle of the Bulge is considered one of the bloodiest battles of World War II. (Read about it (with photos and maps) at archives.gov)
Casualty estimates for the battle vary:
- U.S. Department of Defense: 19,000 American forces killed, 47,500 wounded and 23,000 missing.
- U.S. Department of the Army lists 19,246 American forces killed, 62,489 wounded, and 26,612 captured or missing, though this incorporates losses suffered during the German offensive in Alsace, Operation “Nordwind.”
- British casualties totaled 1,400 with 200 deaths.
- The German High Command estimated 12,652 German troops killed, 38,600 were wounded, and 30,582 were missing. (Allied estimates on German casualties range from 81,000 to 103,000 – some as high as 125,000.) from wikipedia
Resources
Read a 2019 article: 75th anniversary of Battle of the Bulge (Dec. 2019)
Read several first-hand accounts at: battleofthebulge.org.
Read “The story of the “Nuts” reply.
Universal News released this clip on Jan. 11, 1945, reporting on the Battle of the Bulge in Europe.:
Universal News released this clip on Jan. 29, 1945, reporting on the Battle of the Bulge in Europe:
From Simple History: The Battle of the Bulge (1944-45):
Daily “Answers” emails are provided for Daily News Articles, Tuesday’s World Events and Friday’s News Quiz.