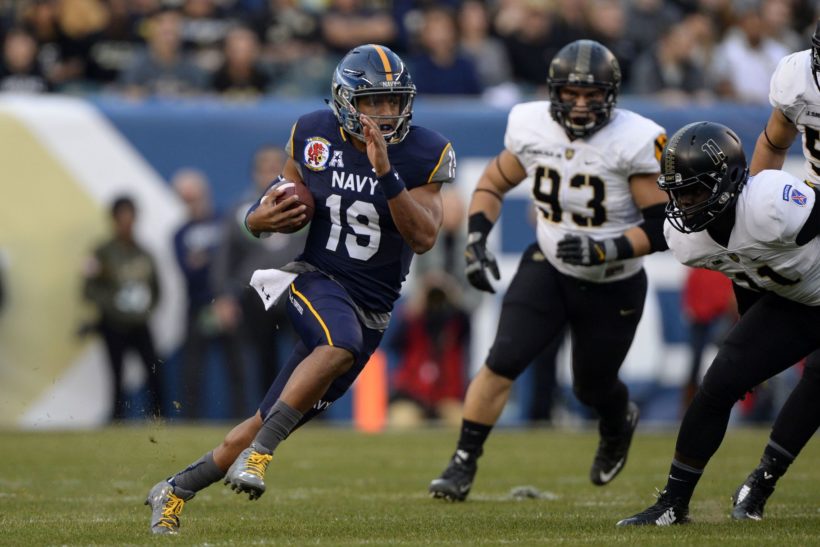
Keenan Reynolds was a star quarterback for the U.S. Naval Academy
redo Jump to...
print Print...
Esper signed a memo on November 8 laying out the new guidelines, which says the athletes must get approval from the defense secretary, and it requires them to eventually fulfill their military obligation or repay the costs of their education.
The memo, obtained by The Associated Press, came at the request of President Trump, who directed the Pentagon in June to come up with a way to allow athletes to play professional sports immediately upon graduation. Trump gave the Pentagon four months to develop the new policy.
Allowing athletes to delay service has been a hotly debated issue. The Obama administration put a policy in place allowing some athletes to go to the pros and defer their military service.
That policy allowed Navy quarterback Keenan Reynolds to be drafted by the Baltimore Ravens in the sixth round of the 2016 draft after completing a four-year run with the Midshipmen. But the year after he went pro, the Defense Department rescinded the policy.
Then-Defense Secretary Jim Mattis, in an April 2017 memo, said that the service academies “exist to develop future officers,” and that graduates would serve as “full-fledged military officers carrying out the normal work and career expectations” of someone who received an education at the taxpayers’ expense.
Earlier this year, however, Trump said he was considering allowing athletes to get a waiver so they could play pro sports. He made the announcement during a Rose Garden ceremony in May when he presented the Commander-in-Chief’s Trophy to the football team of the U.S. Military Academy at West Point. The Army Black Knights completed an 11-2 season and earned the trophy for the second consecutive year.
He issued the order in June, saying that athletes graduating from the academies and Reserve Officers’ Training Corps (ROTC) should be able to defer their military service obligations due to the “short window of time” they have to “take advantage of their athletic talents during which playing professional sports is realistically possible.”
In the new memo, Esper says that military service secretaries can nominate an athlete for a waiver after determining there “is a strong expectation that a Military Service Academy cadet or midshipman’s future professional sports employment will provide the DoD with significant favorable media exposure likely to enhance national level recruiting or public affairs missions.”
If approved by the defense secretary, the athlete must agree to return to the military and serve their enlistment time, which is usually five years. While in the pro sports job, the athlete’s waiver would be reviewed every year.
If the athletes can’t pass required medical standards when it is time to rejoin the military, then they are “encouraged” to serve in a civilian post within the department for no less than five years, according to Esper’s memo. If they choose not to do that they would be subject to repayment of their school expenses.
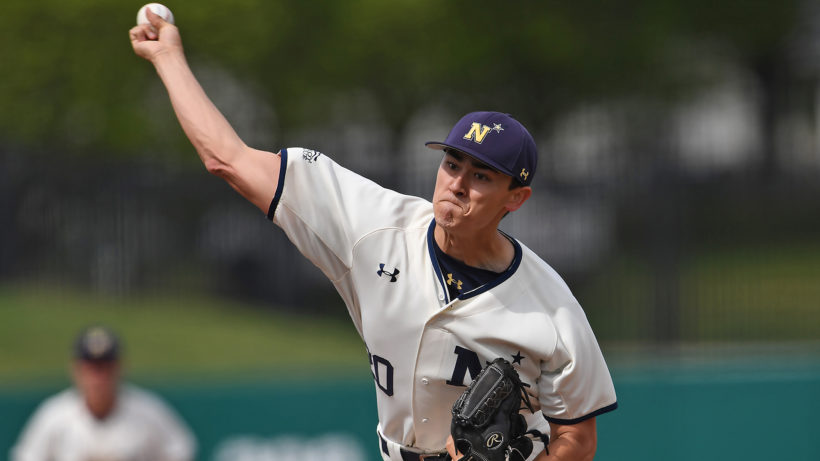
It wasn’t clear Thursday what impact Esper’s new policy will have on the fate of Noah Song, a pitcher from the US Naval Academy. Song, 22, was the fourth-round draft pick this year of the Boston Red Sox, so he is not covered by the new memo. The right-hander was going to pitch for the minor league team in Lowell during the summer before reporting for duty to train as a flight officer.
Song is seeking a waiver but there has been no decision yet. The Navy declined to provide any other details.
Several Navy football players have gone on to have success in the NFL, most notably 1963 Heisman Trophy winner Roger Staubach, a quarterback for the Midshipmen from 1962-64. After serving a tour of duty in Vietnam, he joined the Dallas Cowboys in 1969 and guided the team to a pair of Super Bowl victories.
Another Heisman Trophy winner, Glenn Davis of Army in 1946, was a first-round draft pick of the Detroit Lions but had to serve three years in the Army before making his NFL debut with Detroit in 1950.
In addition, receiver Phil McConkey played for Navy from 1975-78, then served for five years before the New York Giants made him a 27-year-old rookie in 1984. He caught a touchdown pass in the Super Bowl for New York and remained in the NFL through 1989.
This AP story published at most news outlets. Reprinted here for educational purposes only. May not be reproduced on other websites without permission from Associated Press.
Questions
1. The first paragraph of a news article should answer the questions who, what, where and when. List the who, what, where and when of this news item. (NOTE: The remainder of a news article provides details on the why and/or how.)
2. Describe the details of the new policy for academy and ROTC athletes.
3. Why did Secretary Esper implement the new guidelines?
4. a) What was the policy on military athletes going pro under President Obama?
b) Who rescinded Obama’s policy? For what reason did he do so?
5. What is President Trump’s reasoning for implementing this policy?
6. Consider the conditions placed upon athletes who receive a waiver to go pro, as well as Secretary Esper’s stipulation for determining eligibility – and the president’s reason for allowing military athletes to go pro, as well as Gen. Mattis’ opposition. What do you think? Should those in military academies and ROTC be able to defer duty while going pro? Explain your answer.
Daily “Answers” emails are provided for Daily News Articles, Tuesday’s World Events and Friday’s News Quiz.