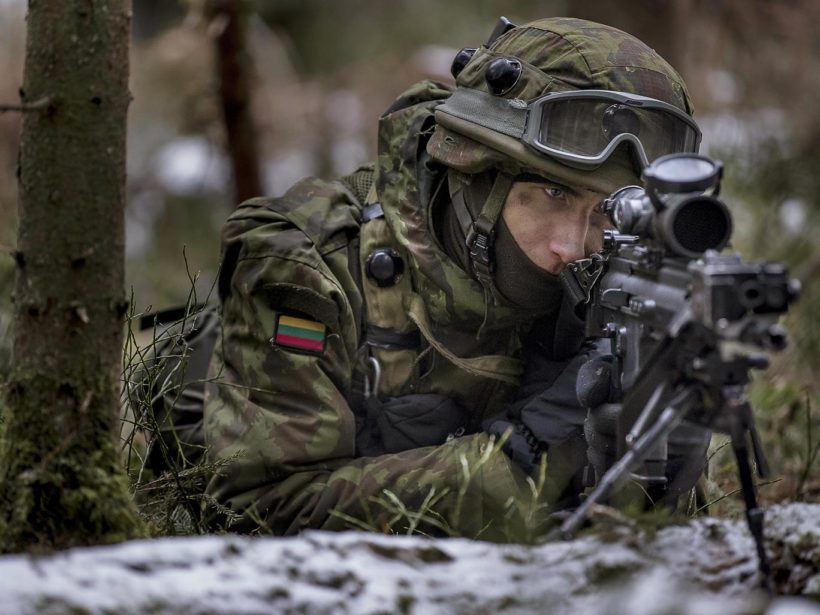
A Lithuanian soldier practices during a NATO military exercise, 'Iron Sword,' at the Rukla military base some 80 miles west of the capital Vilnius, Lithuania.
redo Jump to...
print Print...
(Associated Press at Detroit News) WARSAW, Poland — The United States has decided to accelerate the deployment of troops to Poland, the Baltic states and Romania as part of raising the security of the region, Polish and U.S. defense officials said Wednesday
Polish Defense Minister Antoni Macierewicz made the announcement following talks with the commander of U.S. land troops in Europe, Lt. Gen. Ben Hodges, in Zagan, western Poland, where some of the troops will be deployed. It will be an Armored Brigade Combat Team from Fort Carson, Colorado. Another U.S. force, a battalion, will be deployed April 1 to Orzysz, in the northeast.
Hodges said the troops will arrive in the German port of Bremerhaven on Jan. 6 and will be immediately deployed to Poland, the Baltic states and Romania. Their transfer will be timed and treated as a test of “how fast the force can move from port to field,” he said.
“I’m confident in the very powerful signal, the message it will send (that) the United States, along with the rest of NATO, is committed to deterrence*,” Hodges said. [*Deterrence – a military strategy which uses the threat of retaliation effectively to prevent an attack from an enemy.]
He said the armored brigade has already moved out of its Colorado base and is loading on ships.
“I’m excited about what my country is doing and I’m excited about continuing to work with our ally, Poland,” Hodges said.
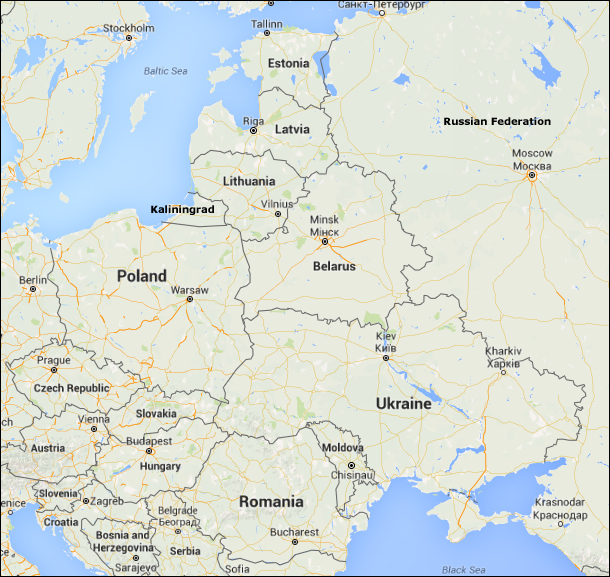
Poland and the Baltic nations of Lithuania, Latvia and Estonia have been uneasy about increased Russian military operations in the region, especially after its 2014 annexation [take control] of Crimea from Ukraine, and have requested U.S. and NATO troops’ presence on their territory as a deterrent. The alliance and the U.S. insist the troop presence is not aimed against anyone, but Russia has threatened measures in response.
The U.S. troops had previously been expected in mid- or late January.
“I am very happy that a decision has been taken by the U.S. side for an earlier deployment,” Macierewicz said.
Reprinted here for educational purposes only from an Associated Press story. May not be reproduced on other websites without permission from Detroit News. Visit the website at detroitnews .com.
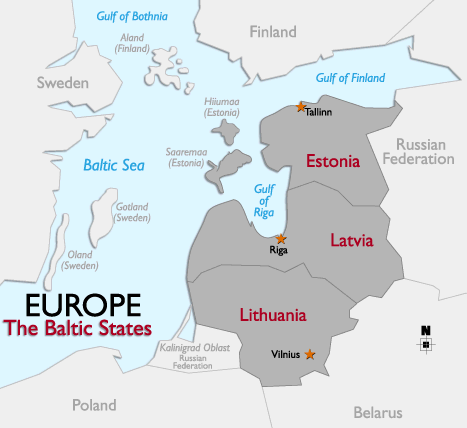
The Baltic States are located in north-central Europe, on the eastern edge of the Baltic Sea, and along the western border of the Russian Federation and Belarus. The Baltic countries of Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania gained their independence from the former U.S.S.R. in 1991. Prior to World War II, Finland was occasionally deemed the fourth Baltic state by Nazi Germany.
Questions
1. The first paragraph of a news article should answer the questions who, what, where and when. List the who, what, where and when of this news item. (NOTE: The remainder of a news article provides details on the why and/or how.)
2. a) Who is Lt. Gen. Ben Hodges?
b) What message does Gen. Hodges say the troop deployment will send?
3. a) What are the Baltic states?
b) Why are Poland and the Baltic states concerned about Russian military operations in the region?
4. a) What is the purpose of NATO?
b) What effect do Poland and the Baltic states think the U.S. and NATO troops will have on the region?
5. Britain’s Independent News reported:
“Across Lithuania, Latvia and Estonia, fears are intensifying that Moscow, after displaying its military might over the past several years in Georgia, Ukraine and now Syria, could have the Baltic states in its sights next. Russian President Vladimir Putin has warned he wouldn’t hesitate to defend Russians wherever they live, words that feel like threats since significant numbers of ethnic Russians live in the Baltics. Whether the danger is real or just bluster remains to be seen.
To be pro-active, young Lithuanian civilians are learning counterinsurgency tactics on weekends. Others have taken steps to protect themselves. The government, in response to pleas from a fearful public, has issued a preparation manual.
Poland is creating a Territorial Defense Force to train thousands of volunteers for the kind of low-intensity hybrid warfare seen in eastern Ukraine, including cyber warfare. Also, some of the new volunteers will be assigned to protect Polish territory near Kaliningrad.”
President-elect Trump has said he would work with Russia’s president Vladimir Putin – that we share the same goal of destroying Islamic terrorists. He has also said that he might not automatically defend the Baltic states – that the U.S. is not the world’s police. It remains to be seen what position he will definitely take.
Do you think Poland and the Baltic states should prepare to defend themselves should Putin send in troops, or should it be up to the U.S. to be their protector? [Note: This is a very general question, as it is really a more complicated foreign policy issue. But overall, in what way do you think the U.S. should back our allies: with troops? provide their troops with military equipment, training and ammunition? Economic sanctions places on aggressive governments like Russia? Through diplomacy?] … Explain your answer.
Background
The brigade combat team (BCT) is the basic deployable unit of maneuver in the US Army:
- A brigade combat team consists of one combat arms branch maneuver brigade, and its assigned support and fire units.
- “The Brigade is normally commanded by a Colonel (O-6) although in some cases a Brigadier General (O-7) may assume command.”
- A brigade combat team carries with it support units necessary to sustain its operations away from its parent division.
- BCTs contain organic artillery support, formerly received from the division artillery (DIVARTY).
- Currently, the U.S. Army is structured around the brigade combat team.
The armored brigade combat team is the army’s primary armored force:
- It was designed around combined arms battalions that contain both M1 Abrams tanks and M2 Bradley infantry fighting vehicles (IFVs).
- Other vehicles, such as HMMWVs and variants of the M113 armored personnel carrier, operate in a supporting role.
- In the future, it will also contain vehicles from the Future Fighting Vehicle and the Armored Multi-Purpose Vehicle.
- An armored brigade combat team consists of seven battalions: three combined arms, one cavalry (reconnaissance), one artillery, one engineer and one brigade support battalion. [A battalion consists of 300 to 800 soldiers and is divided into a number of companies. A battalion is typically commanded by a lieutenant colonel.]
- As of 2014, the armored brigade combat team is the largest brigade combat team formation with 4,743 soldiers. (Prior to 2012, the armored brigade combat team was named the heavy brigade combat team.)
- An ABCT includes 90 Abrams tanks, 90 Bradley IFVs, and 112 M113 vehicles.
(from wikipedia)
NATO:
- The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) is an alliance of 28 countries from North America and Europe committed to fulfilling the goals of the North Atlantic Treaty signed on April 4, 1949.
- In accordance with the Treaty, the fundamental role of NATO is to safeguard the freedom and security of its member countries by political and military means. (from nato.int)
- NATO was established to counter the risk that the Soviet Union would seek to extend its then-control of Eastern Europe to other parts of the continent.
- NATO’s role as a political and military alliance was to provide for collective defense against any form of aggression and to maintain a secure environment for the development of democracy and economic growth.
- NATO is committed to the peaceful resolution of disputes. If diplomatic efforts fail, it has the military capacity needed to undertake crisis-management operations. These are carried out under Article 5 of the Washington Treaty – NATO’s founding treaty – or under a UN mandate, alone or in cooperation with other countries and international organizations. (from nato.int)
- Go to NATO’s website for a list of member countries here.
Daily “Answers” emails are provided for Daily News Articles, Tuesday’s World Events and Friday’s News Quiz.